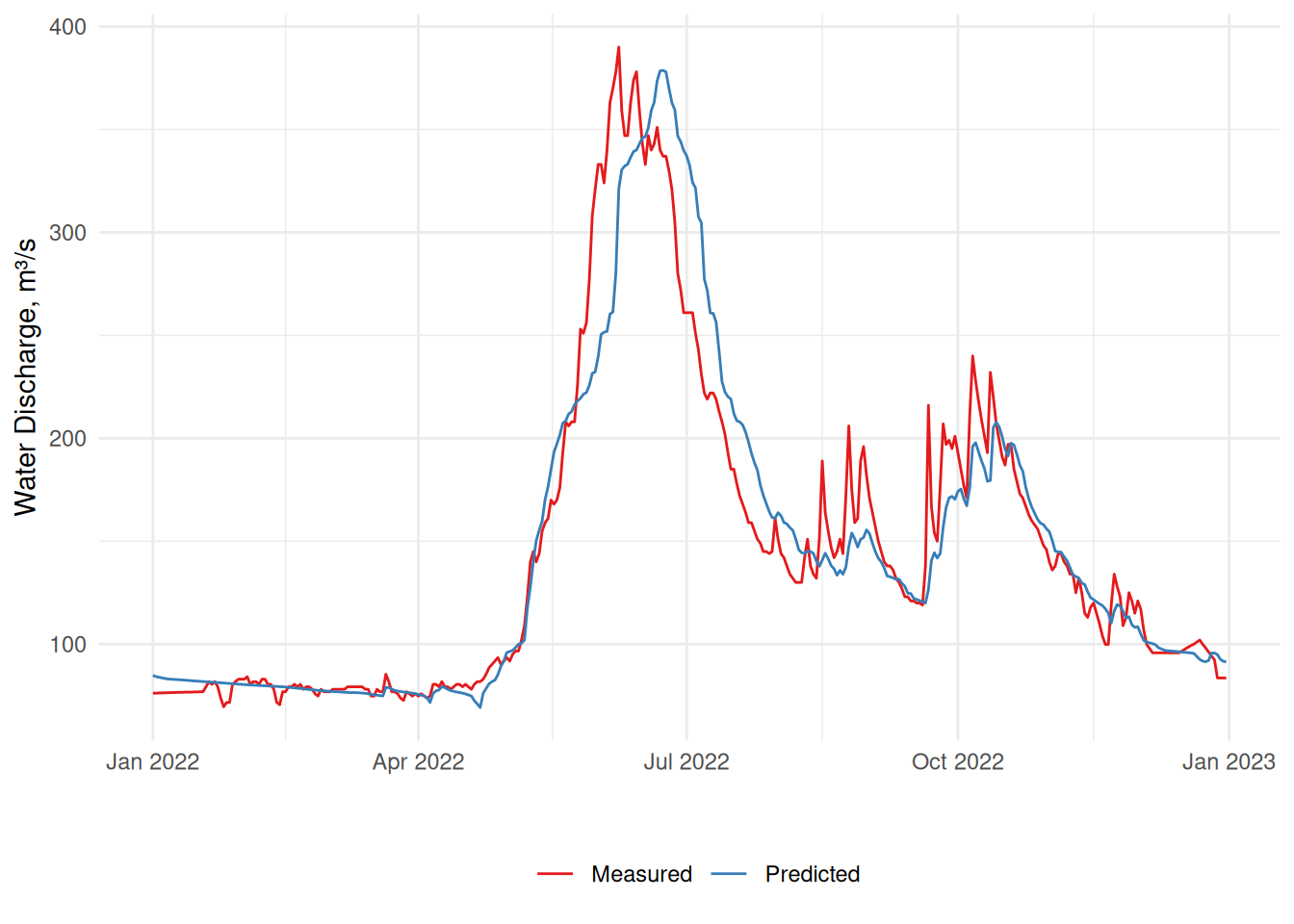
The package includes the mean daily water discharge values (obs in m³/s) measured at the state gauging station Avacha River — Elizovo City (site No. 2090). Alongside the measured water discharge, the mean water discharge in the last 24 hours derived from the GloFAS-ERA5 v4.0 reanalysis is provided (sim).
Example usage
One can estimate the desired metrics using the tidyverse syntax. For example, to get the Nash-Sutcliffe Efficiency (\(NSE\)) or Modified Kling-Gupta Efficiency (\(KGE'\)) for the avacha dataset, one can run:
nse(avacha, obs, sim)
#> # A tibble: 1 × 3
#> .metric .estimator .estimate
#> <chr> <chr> <dbl>
#> 1 nse standard 0.895
kge2012(avacha, obs, sim)
#> # A tibble: 1 × 3
#> .metric .estimator .estimate
#> <chr> <chr> <dbl>
#> 1 kge2012 standard 0.947
Or using the yardstick helper functions, one can create a metric set, combining it with other yardstick metrics, such as \(R^2\):
library(yardstick)
hydro_metrics <- metric_set(kge, pbias, rsq)
hydro_metrics(avacha, obs, sim)
#> # A tibble: 3 × 3
#> .metric .estimator .estimate
#> <chr> <chr> <dbl>
#> 1 kge standard 0.947
#> 2 pbias standard 0.0540
#> 3 rsq standard 0.898
Such syntax is particularly useful when running a group analysis, for example, estimating model performance for different months:
library(lubridate)
library(dplyr)
avacha |>
mutate(month = month(date)) |>
group_by(month) |>
nse(obs, sim)
#> # A tibble: 12 × 4
#> month .metric .estimator .estimate
#> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <dbl>
#> 1 1 nse standard -2.78
#> 2 2 nse standard 0.180
#> 3 3 nse standard 0.0335
#> 4 4 nse standard -0.00438
#> 5 5 nse standard 0.815
#> 6 6 nse standard -2.78
#> 7 7 nse standard -0.244
#> 8 8 nse standard -0.228
#> 9 9 nse standard 0.359
#> 10 10 nse standard 0.466
#> 11 11 nse standard 0.439
#> 12 12 nse standard 0.455
Alternatively, one can still use the vectorised versions of the metrics, ending with the *_vec suffix:
nse_vec(truth = avacha$obs, estimate = avacha$sim)
#> [1] 0.895008